Game design intricately balances art and science, essential for creating captivating experiences. It begins with identifying a core mechanic that governs player interaction, like shape rotation in Tetris. Setting clear goals guides players through the adventure, offering structure and motivation. Here, accessibility matters; games should be easy to grasp initially but grow progressively challenging. Ensuring smooth gameplay flow allows players to immerse themselves fully. Feedback is vital as it informs players of their progress while rewards enhance satisfaction. Balancing difficulty keeps engagement high without frustration. Finally, meaningful missions and effective sound design deepen immersion, making each game enjoyable and memorable for all involved.
Design Your Game Around a Core Mechanic
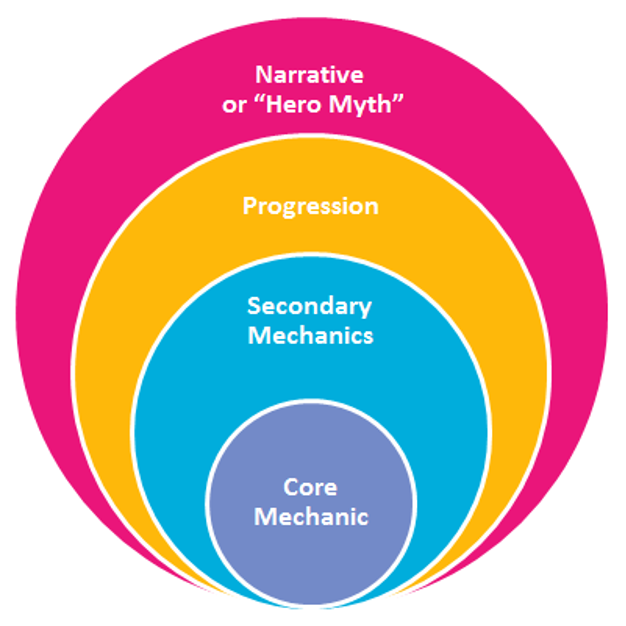 Credits: tkdev.dss.cloud
Credits: tkdev.dss.cloud
Every game revolves around a core mechanic, which serves as the main way players interact with the game. This mechanic is essential, as it shapes the entire gameplay experience. For example, in Tetris, the core mechanic revolves around rotating and placing falling blocks to create complete lines. In contrast, The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild centers on exploration and puzzle-solving using various tools and abilities. To create an engaging game, it’s crucial to refine this core mechanic. It should be simple enough for players to understand quickly, yet deep enough to allow for mastery and strategic thinking. A well-designed core mechanic not only keeps players engaged but also becomes the hallmark of the game, often determining its success. The key is to ensure that all other elements of the game, such as levels, challenges, and rewards, align with and enhance this core mechanic.
Set Clear Goals and Objectives
Setting clear goals and objectives is crucial in game design as it gives players a sense of direction and purpose. When players understand what they need to achieve, it enhances their engagement and motivates them to keep playing. For instance, in The Legend of Zelda, the primary goal is to rescue Princess Zelda, while players also encounter various side quests that provide additional challenges and rewards. These smaller objectives not only enrich the gameplay experience but also help in pacing the game, making it less overwhelming. Moreover, clear objectives can guide players through the game’s narrative and mechanics, ensuring they feel a sense of accomplishment as they progress. A well-structured game will balance these goals, allowing players to feel challenged yet capable, which is key to maintaining their interest.
- Define what success looks like for players
- Establish short-term and long-term goals
- Ensure goals align with game mechanics
- Create variety in objectives to maintain engagement
- Use objectives to guide player progression
- Include both primary and secondary goals
- Allow for player choice in how they fulfill objectives
Make Your Game Easy to Learn, but Challenging to Master
 Credits: 80.lv
Credits: 80.lv
A game should welcome new players with open arms, allowing them to grasp the fundamental mechanics without feeling overwhelmed. The tutorial phase is critical; it should introduce basic controls and gameplay elements in an engaging way. For instance, in Super Mario Bros., players quickly learn how to jump and run, which sets the stage for more complex maneuvers later. However, as they progress, the game introduces challenging levels and enemies that require skill, timing, and strategy. This gradual increase in difficulty maintains interest and encourages players to hone their skills. The idea is to create a learning curve that feels natural, where players can easily grasp the basics but must invest time and effort to master advanced techniques. This balance keeps players returning, as they feel a sense of achievement when overcoming tougher challenges.
Maintain Game Flow and Player Experience
Maintaining game flow is crucial for keeping players engaged. The gameplay should feel smooth, with minimal interruptions that could break immersion. For instance, if a player frequently has to pause to navigate confusing menus, it detracts from their experience. Intuitive controls and a user-friendly interface can help players stay focused on the game itself.
Moreover, the pacing of the game should align with the player’s expectations. If a game is too slow, players may lose interest; if it’s too fast, they can feel overwhelmed. A good example is Celeste, where the level design encourages quick reflexes but also allows players to learn from their mistakes without feeling punished.
Additionally, ensuring that the game provides a consistent experience across various scenarios is important. For example, if a player can easily perform actions in one part of the game, they should be able to replicate that in others. This consistency builds player confidence and enhances their overall enjoyment.
Offer Feedback and Rewards
Feedback is essential in games as it helps players understand their actions and progress. For example, when a player successfully completes a level, immediate visual effects like fireworks or a clear sound cue can enhance the feeling of accomplishment. Similarly, when players make mistakes, subtle feedback, such as a character’s reaction or a sound indicating failure, can guide them to improve.
Rewards also play a crucial role in maintaining player motivation. These can come in various forms, such as unlocking new levels, earning in-game currency, or receiving achievements. Games like Candy Crush Saga use a system of stars to reward players based on their performance in each level, encouraging them to replay levels to achieve better results. A well-structured reward system not only keeps players engaged but also encourages them to invest more time into the game.
Balance the Game
Balancing a game involves adjusting its difficulty to create an engaging experience for all players. It’s important that players feel challenged but not overwhelmed. For example, in a platformer game, if all levels are too easy, players may quickly lose interest. Conversely, if levels are too hard, they may become frustrated and give up. Incorporating varying difficulty levels can help here. For instance, in Dark Souls, players can choose how to approach enemies and bosses, allowing for different strategies based on their skill levels. This flexibility keeps players invested and encourages them to try again even after failure. Additionally, implementing mechanics like power-ups or skill upgrades can help balance the game by giving players tools to overcome tougher challenges. Ultimately, achieving the right balance makes the game enjoyable and rewarding for everyone.
| Strategy | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Paths | Offering players different ways to approach challenges depending on their skill level. | Games like *The Legend of Zelda* allow players to choose different dungeons in various orders. |
| Varied Difficulty Levels | Providing adjustable difficulty settings to cater to diverse player experiences. | Many modern games like *Resident Evil* let players choose their preferred difficulty before starting. |
| Skill-based Challenges | Incorporating challenges that require different skills to succeed, accommodating various play styles. | Games like *Overwatch* have characters that cater to players with different approaches. |
| Dynamic Scaling | Adjusting the game’s difficulty based on player performance to maintain a balanced challenge. | *Dark Souls* series uses mechanics that can adjust enemy strength based on player actions. |
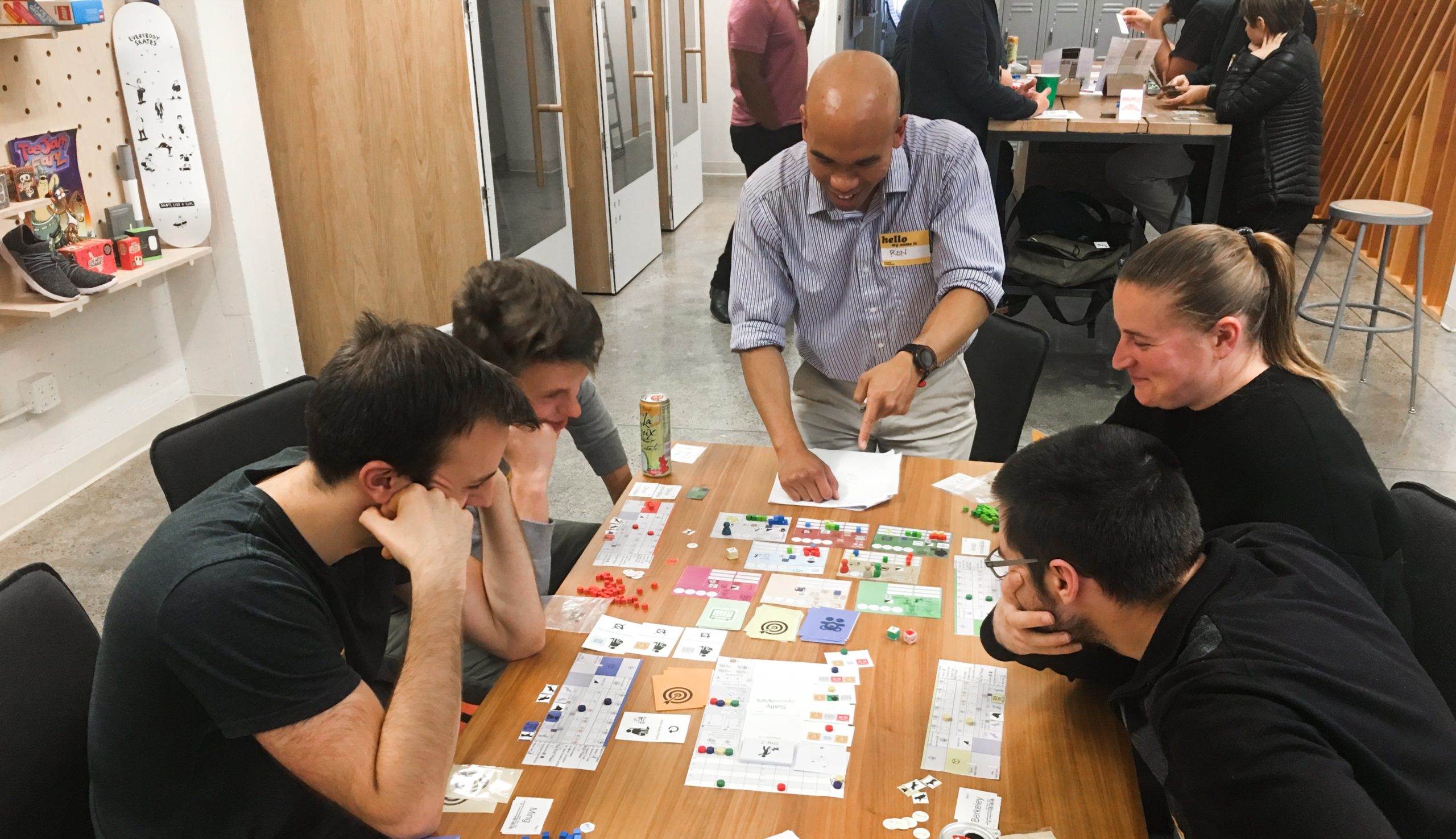
Playtesting
 Credits: backerkit.com
Credits: backerkit.com
Playtesting is a vital component of game design that allows developers to see how their game performs in real-world scenarios. By observing players as they interact with the game, designers can identify areas that work well and those that need improvement. This feedback is invaluable for refining game mechanics, balancing difficulty, and ensuring that the overall experience is enjoyable.
For example, during playtesting a platformer game, designers might notice that players struggle at a particular jump. This feedback can prompt adjustments to the level design or the mechanics of jumping to enhance player experience. Additionally, playtesting can reveal if players are confused by certain game elements, such as unclear instructions or poorly designed interfaces.
It’s essential to conduct playtests at various stages of development, from early prototypes to near-final versions. This iterative process helps catch issues early and allows developers to make informed decisions based on actual player behavior rather than assumptions. To get the most out of playtesting, developers should aim to create a comfortable environment for testers, encouraging honest feedback without the fear of hurting feelings. Ultimately, effective playtesting can significantly elevate a game’s quality and player satisfaction.
Sound Design
Sound design is an integral part of game development that often gets sidelined, yet it profoundly impacts player experience. Good sound design includes not only background music that sets the mood but also sound effects that provide feedback and enhance gameplay. For example, the satisfying sound of collecting coins in Super Mario gives players immediate feedback on their actions, reinforcing positive behavior. Similarly, the eerie soundscapes in horror games like Silent Hill heighten tension and immersion, making players feel more engaged with the environment.
Moreover, sound cues can guide players through challenges. In games like Zelda, the sound of a treasure chest opening signals accomplishment, while specific audio cues might indicate nearby dangers or hidden paths. This auditory guidance helps players make decisions and enhances their overall sense of agency in the game.
In multiplayer games, sound design can also play a strategic role. Hearing the footsteps of an opponent or a gunshot can significantly affect a player’s approach to gameplay, creating a more dynamic and reactive experience. Ultimately, effective sound design enriches the narrative, reinforces gameplay mechanics, and immerses players in the game world, making it a crucial element that should not be overlooked.
Provide Meaningful Core Missions
Meaningful core missions are the backbone of an engaging game. They give players a reason to invest their time and effort into the game. These missions should not only challenge players but also resonate with them emotionally. For instance, in The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild, the main mission to defeat Calamity Ganon is deeply tied to the protagonist’s journey to save Hyrule. This overarching goal drives the player’s actions and decisions throughout the game, making every side quest and exploration feel relevant.
Additionally, missions should evolve as players progress, introducing new layers of complexity and narrative depth. In The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt, Geralt’s quests are often rich with moral choices that impact the story’s outcome, giving players a sense of agency. When players see how their actions shape the game world, they feel more connected to the narrative, thus enhancing their overall experience.
In multiplayer games, core missions can foster collaboration and competition. For example, in Destiny 2, players engage in raids and strikes that require teamwork to complete. These missions not only challenge players but also build a sense of community as they work together to achieve common goals. By providing meaningful core missions, designers can create a framework that keeps players engaged, motivated, and invested in the game.
Utilize Visual Storytelling Techniques
visual storytelling is a powerful tool in game design that helps convey narrative and emotions without relying solely on text or dialogue. By using images, colors, and animations, designers can immerse players in the game’s world and guide them through the story seamlessly. For instance, in Journey, the art direction and color palette are used to reflect the protagonist’s emotional journey, enhancing the player’s connection to the character and the environment. Similarly, in The Last of Us, visual cues such as the decay of the environment and character expressions tell a story of survival and loss, enriching the gameplay experience. Effective use of visual storytelling can make a game feel more alive and engaging, allowing players to interpret and experience the narrative on a deeper level.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main goals of game design?
The main goals of game design include creating fun, engaging experiences, ensuring players feel challenged yet rewarded, and developing a story or objective that keeps players interested.
2. How important is player feedback in game design?
Player feedback is extremely important. It helps designers understand what works well and what needs improvement, allowing them to make the game more enjoyable.
3. What role does balance play in game design?
Balance is crucial in game design because it ensures no character, strategy, or game element is too powerful or too weak, making the game fair and enjoyable for all players.
4. How can a game designer create a memorable character?
To create a memorable character, a designer should give the character a unique personality, relatable traits, and a compelling backstory that players can connect with.
5. What is the significance of game mechanics?
Game mechanics are the rules and systems that govern how a game operates. They are significant because they drive player interaction and help build the overall experience of the game.
TL;DR This blog post outlines essential principles of game design, emphasizing the importance of core mechanics, clear goals, accessible difficulty, seamless gameplay flow, effective feedback and rewards, game balance, playtesting, impactful sound design, and meaningful core missions. By applying these principles, game designers can create engaging and immersive experiences that resonate with players.

