Xeriscaping is a sustainable gardening method that helps reduce the need for watering, making it especially valuable in dry regions. This guide outlines how to create your own xeriscape space, starting with assessing your yard’s sunlight and moisture levels. Next, you’ll sketch a design while grouping plants by their water needs. Improving soil quality is essential, so testing pH and adding organic material are recommended steps. Choosing native plants ensures they’re well-suited to your environment. Lastly, implementing hardscapes, efficient irrigation methods like drip systems, and regular maintenance will keep your xeriscaped garden thriving while conserving water effectively.
What is Xeriscaping?
Xeriscaping is a landscaping method that aims to minimize the need for irrigation by using drought-resistant plants and efficient design techniques. The term comes from the Greek word “xeros,” which means dry. This approach is especially useful in areas with limited water supply or where drought is common. By selecting plants that are native to the local environment, homeowners can create gardens that are both beautiful and sustainable. These plants are adapted to thrive in the natural conditions of the region, reducing the need for extra watering and care. Xeriscaping not only helps to conserve water but also promotes biodiversity by providing habitats for local wildlife.
Benefits of Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping offers numerous advantages that make it an appealing choice for homeowners, especially in regions facing water scarcity. One of the primary benefits is water conservation; xeriscaped gardens can reduce irrigation needs by up to 50%. This is achieved through the use of drought-tolerant plants that require less water and by grouping plants according to their water needs, which optimizes irrigation efforts. Additionally, xeriscaping promotes environmental protection. With fewer chemicals like fertilizers and pesticides required, there is a significant reduction in soil and water pollution, leading to healthier ecosystems.
Moreover, xeriscaping encourages biodiversity by providing habitats for local wildlife. Using native plants not only supports local fauna but also enhances the resilience of the garden, as these plants are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. Financially, xeriscaping can lead to cost savings over time, as lower water bills and reduced maintenance efforts contribute to a more economical landscape. Lastly, xeriscaped gardens can be aesthetically pleasing, showcasing a diverse array of plants and creative hardscape designs that enhance the beauty of outdoor spaces.
- Reduces water usage
- Low maintenance requirements
- Saves money on water bills
- Enhances property value
- Provides habitat for local wildlife
- Protects local ecosystems
- Offers aesthetic diversity with native plants
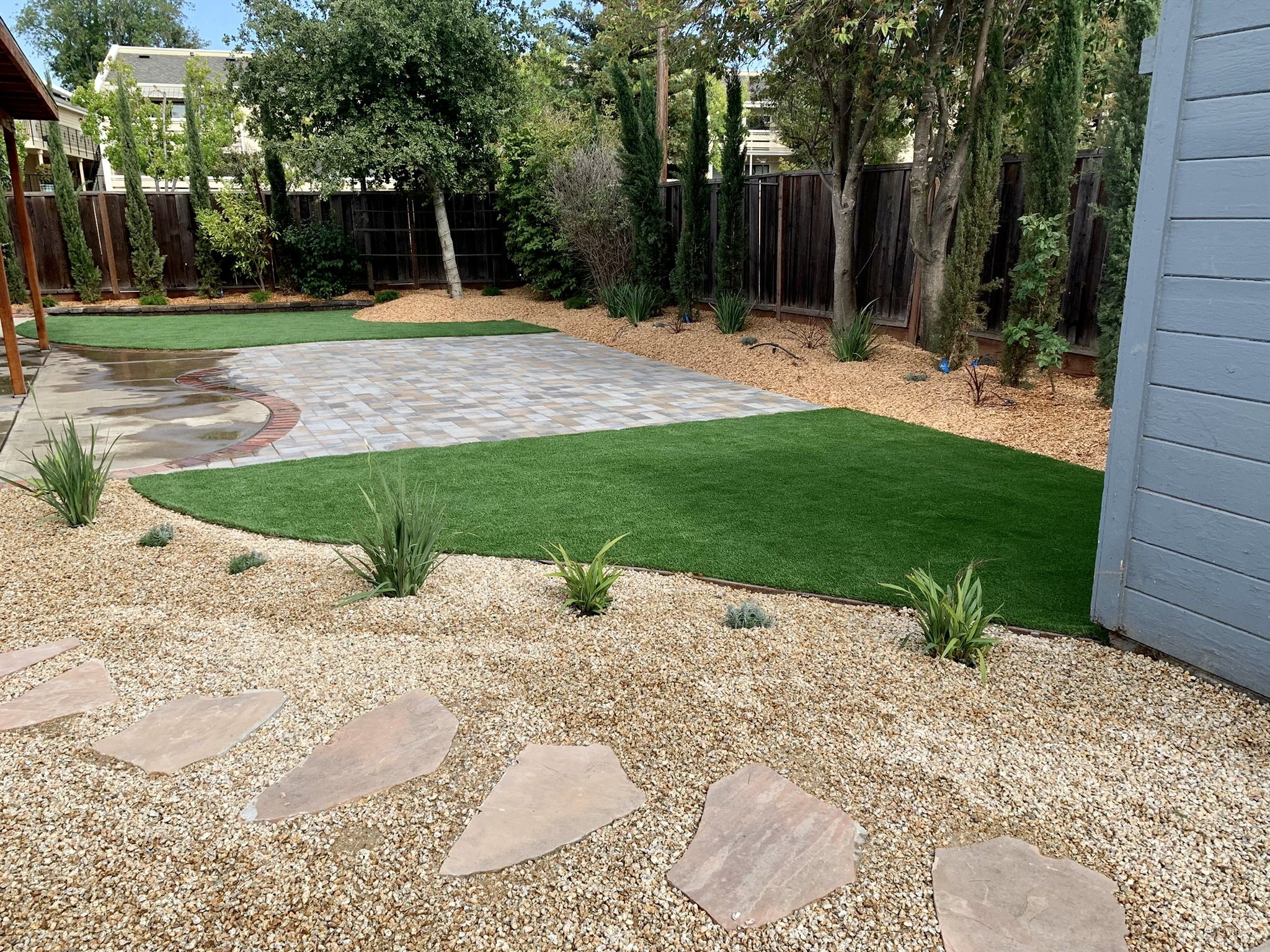
Step 1: Assess Your Yard
 Credits: yardzen.com
Credits: yardzen.com
Start by taking a good look at your yard. Walk around at different times of the day to see how sunlight moves across your space. Identify areas that get full sun, partial sun, and shade. It helps to sketch a simple map on graph paper to visualize these zones. Next, consider the moisture levels in your yard. After rainfall or watering, observe where water collects and how quickly it dries. This will help you designate hydrozones—areas that you can classify as high, moderate, or low-water use zones. Knowing these details is crucial for planning a xeriscape garden that thrives with minimal irrigation.
Step 2: Plan Your Design
 Credits: desertxeriscape.wordpress.com
Credits: desertxeriscape.wordpress.com
Start by sketching a basic layout of your yard on graph paper. This should include existing features such as trees, patios, and pathways. Visualizing these elements will help you understand how to incorporate new plants and hardscape features into your design. Next, group your plants based on their water needs. Create distinct zones for low-water, moderate-water, and high-water plants. This is essential for efficient irrigation and helps ensure that each plant receives the appropriate amount of moisture. For example, you might place drought-tolerant succulents in a sunny, low-water zone and shade-loving ferns in a cooler, higher-water area. This strategic grouping will not only optimize water usage but also enhance the overall look of your xeriscape garden.
Step 3: Improve Your Soil
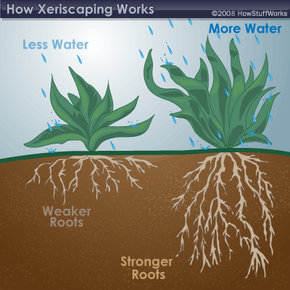
Improving your soil is crucial for the success of your xeriscape garden. Start by testing your soil’s pH using a simple soil test kit. This will help you understand if your soil is too acidic or alkaline. If adjustments are needed, you can add lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it. Next, enhance your soil’s structure and fertility by incorporating organic matter. Mixing in compost not only improves nutrient availability but also increases water retention and drainage. A good mix of organic mulch, such as shredded bark or wood chips, can also help keep the soil cool and moist. This creates a healthier environment for your plants to thrive, especially during dry spells.
Step 4: Select Your Plants
Choosing the right plants is crucial for a successful xeriscape garden. Start by looking for native plants that are suited to your local climate. Native plants are adapted to your area’s soil and weather conditions, which means they require less water and maintenance. You can consult local gardening centers or online resources to find lists of drought-tolerant plants specific to your region.
When selecting plants, consider their growth habits and the amount of sunlight they will receive in your garden. Group plants with similar water needs together, which will make it easier to manage their irrigation. For example, in a sunny area, you might choose heat-loving plants like lavender and agave, while shaded spots could feature ferns and hostas that thrive in lower light.
Additionally, think about the colors, textures, and heights of the plants to create a visually appealing layout. Mixing perennials and annuals can provide year-round interest. Incorporating ground covers can also help reduce weeds and retain moisture. Always remember to check the mature size of the plants to avoid overcrowding later on.
Step 5: Remove Existing Grass
Removing existing grass is an essential step in creating your xeriscape garden. Start by deciding on the method that works best for your situation. One straightforward approach is physical removal, where you can use a shovel or a rototiller to dig up the grass along with its roots. This method is effective but can be labor-intensive.
Another option is solarization, which uses heat to kill the grass. To do this, first, mow the grass as short as possible. Then, water the area thoroughly and cover it with clear plastic. Leave it in place for about six weeks; the heat trapped underneath will effectively kill the grass and its roots.
Alternatively, consider sheet mulching. This method involves laying down a thick layer of cardboard or newspaper directly over the grass. Then, cover this with compost and organic mulch. Over time, the materials will break down, smothering the grass and enriching the soil. Each of these techniques will help to prepare your yard for the new drought-tolerant plants you plan to introduce.
Step 6: Install Hardscape Elements
Hardscape elements are essential in xeriscaping as they provide structure and visual interest while minimizing the need for water. Start by creating pathways to connect different areas of your garden. You can use materials like gravel, decomposed granite, or natural stone pavers. These materials allow water to permeate the ground instead of running off, which is beneficial for plant health. Avoid using solid concrete, as it can create a barrier that prevents water from reaching the soil.
Consider adding raised beds made of wood, stone, or bricks. These not only add a decorative touch but can also help with soil drainage and heat retention. You might also install decorative retaining walls that help manage slope and soil erosion while creating planting niches.
Incorporate benches or seating areas made from natural materials to encourage enjoyment of the space. Fire pits or outdoor fireplaces can also enhance the area, making it more inviting for gatherings. Be sure to choose materials that blend well with your chosen plants to create a cohesive look in your xeriscape garden.
Step 7: Set Up Efficient Irrigation
To ensure your xeriscape garden remains vibrant while conserving water, setting up an efficient irrigation system is crucial. A drip irrigation system is one of the best options, as it delivers water directly to the roots of your plants, minimizing evaporation and runoff. You can install it easily by laying out hoses with emitters at intervals that correspond to your plants’ needs. For instance, if you have a row of succulents, you can space the emitters closer together compared to more drought-tolerant flowers that require less frequent watering.
In addition to drip irrigation, consider incorporating rainwater harvesting techniques. Setting up barrels to collect rainwater from your roof can provide a sustainable water source for your garden. This harvested rainwater can be used to supplement your irrigation system during dry spells, ensuring your plants receive the moisture they need without increasing your water bill.
Lastly, be sure to monitor your irrigation system regularly. Adjust the timing and amount of water based on seasonal changes and rainfall. This proactive approach will help you maintain a healthy xeriscape while maximizing water efficiency.
Step 8: Mulch Your Garden
Applying mulch is a crucial step in xeriscaping that helps with water conservation and plant health. Start by spreading 2-4 inches of mulch around your plants, ensuring that it does not touch the stems directly. Organic mulches, like bark, wood chips, or straw, not only retain moisture but also break down over time, enriching the soil. Inorganic options, such as gravel or rock, can also be used and require less maintenance over time. It’s important to replenish your mulch every couple of years to maintain its effectiveness. For instance, if you notice that the mulch has thinned out or decomposed, simply add a new layer to keep your garden healthy and thriving.
Step 9: Maintain Your Xeriscape Garden
To keep your xeriscape garden thriving, focus on deep and infrequent watering. This helps the plants develop strong root systems, making them more resilient. Typically, watering once every two weeks is sufficient, but adjust as needed based on weather conditions. Regular weeding is essential to prevent competition for resources; hand-pulling weeds is often the best method, especially in smaller gardens. Pruning is also important—remove dead or overgrown branches to encourage healthy growth and airflow. When it comes to fertilizing, less is more. Use organic or slow-release fertilizers sparingly, as many native plants are adapted to poorer soils and can thrive without much added nutrition. Keep an eye on your plants and adjust your care routine based on their specific needs.
Common Drought-Tolerant Plants
Choosing the right plants is crucial for a successful xeriscape design. Drought-tolerant plants are those that can survive with minimal water, making them perfect for arid climates. Here are some common options:
In the Oasis Zone, where you might want some shaded areas, consider planting Barrenwort (Epimedium) and Fringed Bleeding Heart (Dicentra eximia). These plants thrive in partial shade and can handle dry spells well.
For the Transition Zone, which experiences a mix of sun and shade, Russian Sage (Perovskia atriplicifolia) is an excellent choice. It has silvery leaves and purple flowers, adding vibrant color while being highly drought-resistant. Fountain Grass (Pennisetum alopecuroides) also works well here, providing not only aesthetic appeal but also some movement in the landscape with its graceful plumes.
In the Xeric Zone, where full sun and very little water are the norm, Lavender (Lavandula) is a standout. Its fragrant blooms attract pollinators and require little care. Sedum, commonly known as stonecrop, is another fantastic option. With its thick, fleshy leaves, it stores water efficiently and comes in many varieties, ensuring year-round interest.
When selecting plants, always consider your local climate and soil conditions. Native plants will often perform the best, as they are adapted to the local environment and require less maintenance.
| Zone | Plant |
|---|---|
| Oasis Zone | Barrenwort |
| Oasis Zone | Fringed Bleeding Heart |
| Transition Zone | Russian Sage |
| Transition Zone | Fountain Grass |
| Xeric Zone | Lavender |
| Xeric Zone | Sedum |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is xeriscaping, and why should I consider it for my garden?
Xeriscaping is a landscaping method that focuses on using drought-resistant plants and efficient watering techniques. It saves water and reduces maintenance, making it great for areas with low rainfall.
2. How do I choose the right plants for a xeriscape design?
Select native or drought-tolerant plants that thrive in your local climate. Look for plants with deep roots, thick leaves, or those that are already adapted to dry conditions.
3. What steps should I follow to design my xeriscape landscape?
Start by assessing your yard, planning layout, preparing the soil, selecting plants, placing mulch, and finally setting up a watering system.
4. How can I make sure my xeriscape stays healthy and looks good?
Regular maintenance is key. Mulch to retain moisture, check plants for pests, and water wisely. Grouping plants with similar needs can also help.
5. Can I mix xeriscaping with existing landscaping features?
Absolutely! You can blend xeriscape principles with your current plants and features. Just make sure your new choices are compatible with existing ones.
TL;DR This guide outlines the steps to create a xeriscape garden, which uses drought-tolerant plants and efficient landscaping to conserve water. Benefits include reducing water use, promoting local biodiversity, and lowering maintenance costs. Follow steps like assessing your yard, planning your design, improving soil, selecting native plants, removing grass, installing hardscapes, setting up irrigation, mulching, and maintaining your garden for a sustainable landscape.

